Why Compliance Matters for USA–India Money Transfers
For NRIs living in the United States, sending money to India is a common financial activity. Whether it is for family support, investments, education expenses, or savings, cross-border transfers must comply with regulations in both the United States and India. While the process is generally smooth, a lack of awareness around compliance requirements can lead to delays, additional verification, or reporting issues.
Understanding the compliance framework helps NRIs send money confidently, avoid regulatory scrutiny, and ensure that transfers are processed without interruption. This guide explains the key compliance rules governing money transfers from the USA to India.
How Cross-Border Transfers from the USA Work
International money transfers from the USA typically involve regulated financial institutions such as banks or licensed money service businesses. These entities are required to follow strict Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CFT) rules.
A standard transfer involves identity verification of the sender, declaration of the purpose of transfer, monitoring of transaction size and frequency, and reporting to authorities where thresholds are crossed. These checks are designed to ensure transparency and traceability in cross-border payments.
Key US Compliance Regulations NRIs Should Know
Money transfers from the USA are governed by several federal regulations.
Under the Bank Secrecy Act, financial institutions are required to maintain transaction records and report certain transfers to prevent financial crime. Anti-money laundering Anti-Money Laundering rules mandate customer due diligence and ongoing monitoring of transactions.
In practice, transactions above USD 10,000 may trigger reporting requirements, and repeated smaller transfers structured to avoid reporting thresholds can attract scrutiny.
Compliance Requirements on the India Side
While the sender complies with US regulations, Indian authorities also monitor inbound remittances. Indian banks classify incoming transfers using purpose codes and may review large or unusual inflows for source verification.
All inbound foreign exchange transactions are governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), which sets the legal framework for foreign currency movements into India.
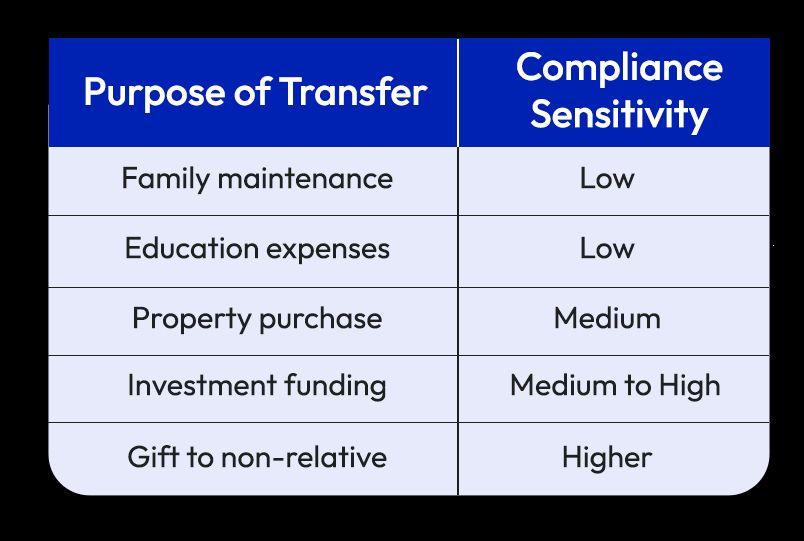
Common Compliance Checks During Transfers
NRIs may encounter additional compliance checks when sending large sums, making frequent transfers, or remitting funds for investment or property-related purposes. In such cases, banks may request supporting documentation such as proof of income, employment details, or clarification on the purpose of remittance. These checks are routine and form part of standard regulatory oversight.
Accurately declaring the purpose of transfer helps reduce delays and ensures smoother processing.
Reporting Obligations for NRIs in the USA
Beyond bank-level reporting, NRIs in the USA may have additional disclosure obligations. US tax residents are required to report worldwide income, and certain thresholds trigger foreign asset disclosures such as FBAR filings.
These reporting requirements are independent of the act of transferring money but are an important part of overall compliance.
What NRIs Can Expect Going Forward
As cross-border payments continue to evolve, there is increasing focus on transparency, speed, and regulatory alignment. Platforms serving NRIs are expanding corridors to meet growing demand.
ScopeX is expected to introduce USD to INR transfers for NRIs in the United States, extending its Europe-to-India remittance offering to the US corridor. This will allow NRIs in the USA to access a remittance experience built around clarity, compliance, and competitive exchange rates once the service goes live.
Common Mistakes NRIs Should Avoid
Common issues include providing vague transfer purposes, attempting to structure transactions to avoid reporting thresholds, ignoring tax reporting obligations, or using unregulated channels. Staying transparent and compliant is always the safest approach.
FAQs: USA to India Money Transfer Compliance
Do all transfers from the USA to India get reported?Not all transfers are individually reported, but banks monitor transactions and report those that meet regulatory thresholds.
Is there a maximum amount I can send from the USA to India?There is no fixed legal cap, but large transfers are subject to enhanced compliance checks.
Do I need to report remittances on my US tax return?Transfers themselves are not taxed, but related income or foreign assets may need to be reported.
Why do banks ask for transfer purpose details?Purpose codes help banks comply with Indian foreign exchange regulations.
Can compliance rules change?Yes. Regulatory authorities may update requirements based on risk assessments.
Final Thoughts
Sending money from the USA to India is a regulated process designed to protect both financial systems. For NRIs, understanding compliance rules on both sides helps avoid delays and ensures smooth transfers.
Clear documentation, accurate declarations, and awareness of reporting obligations remain the foundation of hassle-free cross-border remittances.
Sources & Disclaimer
The information in this article is based on publicly available provider disclosures, marketing materials, industry reports, and general remittance market practices at the time of writing. Exchange rates, fees, transfer speeds, and availability may vary by country, payment method, bank, and time period.
Company names mentioned are included for illustrative and comparative purposes only. Any performance metrics, pricing examples, or user experiences referenced reflect advertised claims or individual reports and should not be treated as guarantees. Readers are encouraged to verify live rates, fees, and terms directly with the service provider before initiating a transfer.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice, investment advice, or a recommendation of any specific service.